
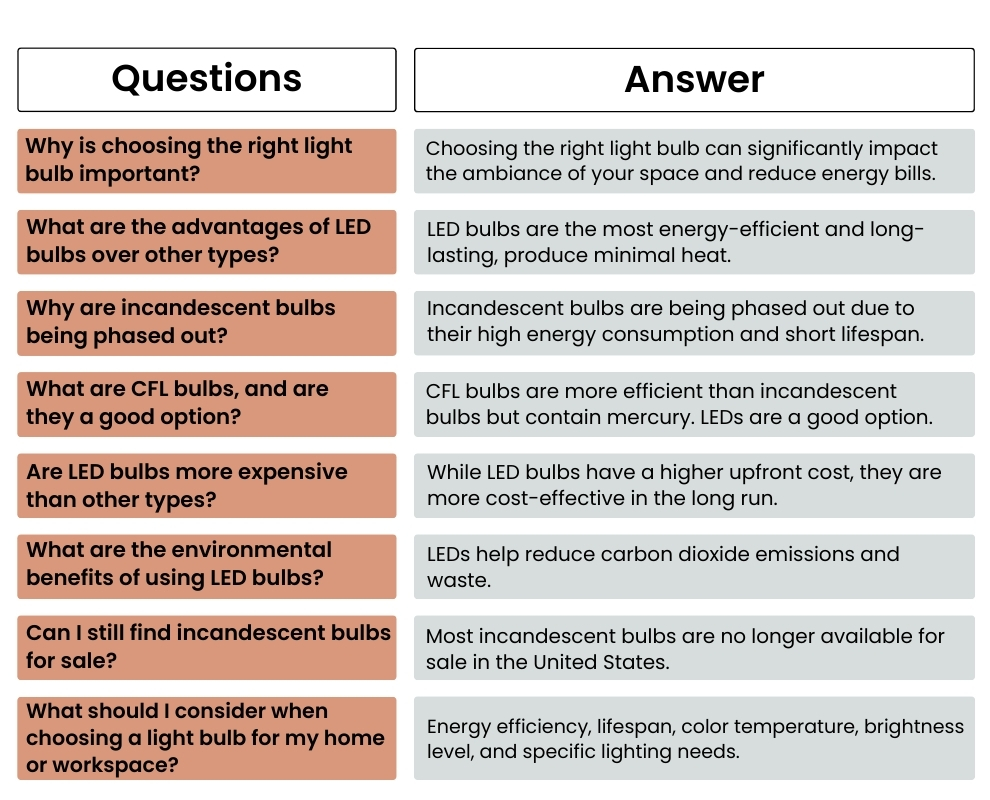
Choosing the right light bulb for your home or workspace can significantly impact both the ambiance and your energy bills. With various types of light bulbs available in the market, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks, it can be overwhelming to decide which one to use. This blog will guide you through the main types of light bulbs—incandescent, halogen, CFL, and LED—so you can make an informed decision.
Historical Evolution of the Light Bulb
Although Thomas Edison is often credited with inventing the light bulb, he was actually the first to patent it in 1879, with others like Joseph Swan also developing similar lamps during that period. The light bulb's concept dates back to the 1830s, and over the past 180 years, the incandescent bulb has evolved, notably with tungsten filaments enhancing its durability. However, due to high energy consumption, incandescent bulbs were phased out in favor of more efficient options like halogen bulbs, first developed in 1955 by Elmer Fridrich and Emmet Wiley. While halogens don't match the energy savings of CFLs or LEDs, they offer a crucial step forward, combining efficiency with the warm glow of traditional lighting.
A Guide to Light Bulbs: Understanding Halogens, Incandescents, LEDs, and CFLs


Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs, a more efficient type of incandescent, offer bright, white light, ideal for focused lighting like desk lamps. They are fully dimmable but can get very hot, posing safety concerns. While more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, they are less so than CFLs and LEDs.
Incandescent Bulbs
Incandescent bulbs, known for their warm light, are inefficient, converting only 10% of energy into light. They have a short lifespan (around 1,000 hours) but remain popular due to their low cost and light quality, though their use has declined with more efficient alternatives.
LED Bulbs
LEDs are the most energy-efficient and long-lasting bulbs, using up to 90% less energy and lasting up to 25,000 hours or more. They produce minimal heat and come in a wide range of color temperatures. Though initially more expensive, they are cost-effective over time due to energy savings.
CFL Bulbs
CFLs use 70-80% less energy than incandescent bulbs and last up to 10 times longer. They provide various color temperatures but contain a small amount of mercury, requiring careful disposal. Despite this, they are popular for their energy savings and longer lifespan.
The End of an Era: Hello Energy Efficiency
It's official: the incandescent light bulb, a staple of American homes since Thomas Edison patented it in the late 1800s, is now a relic of the past. The new energy efficiency rules in the United States mean that shoppers can no longer purchase most incandescent bulbs, marking a significant shift in the way we light our homes.
What to Use Instead: Alternatives to Incandescent and Halogen Bulbs


With incandescent and halogen bulbs being phased out, consumers may wonder about their options. LEDs are the most popular choice, offering a wide range of color temperatures, brightness levels, and designs to fit various needs. For those looking for a softer, warmer light reminiscent of incandescent bulbs, there are LED options designed to mimic that traditional glow.
Other alternatives include compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), although they are also being phased out due to new regulations. LEDs remain the go-to choice for most applications, from ambient lighting in living rooms to task lighting in kitchens and offices.
The Rise of LEDs: Lighting the Way Forward
LED lights, which have already made a significant impact on America's energy landscape, are taking the place of incandescent bulbs. LED, short for light-emitting diode, uses far less power than traditional incandescent bulbs, making them a more energy-efficient choice. This transition isn't just about saving electricity—it's also about saving money and reducing the nation’s carbon footprint.
LEDs have been instrumental in driving down electricity demand in American homes. By using less power, they have helped lower greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major cause of climate change. The new efficiency standards require light bulbs to produce at least 45 lumens per watt, a benchmark that most incandescent bulbs simply can't meet. While a few specialized types of incandescent bulbs, like those used in ovens and bug lights, are exempt, the majority will struggle to comply with these new standards.
Benefits of LED Light Bulbs


Energy Savings and Cost Benefits
Switching from incandescent to LED lighting is akin to replacing a car that gets 25 miles per gallon with one that achieves 130 miles per gallon. The Department of Energy estimates that Americans will collectively save nearly $3 billion a year on their utility bills thanks to these new rules. Cost savings are particularly beneficial for lower-income households, who often spend a larger portion of their income on utilities. Furthermore, LED prices have dropped significantly, making them an affordable option for all consumers.
Environmental Impact
Over the next three decades, the new lighting rules are expected to cut carbon dioxide emissions by 222 million metric tons, comparable to the emissions produced by 28 million homes in one year. This reduction in emissions is critical, as lighting accounts for about 5% of global carbon emissions, with inefficient bulbs contributing more due to the excess heat they produce. LEDs not only use less energy but also last much longer—25 to 50 times longer—than incandescent bulbs, reducing waste and the need for frequent replacements.
Improved Lighting Quality and Flexibility
LEDs provide superior lighting quality compared to incandescent and CFL bulbs. They offer a wide range of color temperatures, from warm to cool light, allowing users to choose the ambiance that suits their needs. Additionally, LEDs can be dimmed without affecting their efficiency, providing greater control over lighting levels and creating versatile environments for various activities. This flexibility makes LEDs suitable for diverse applications, from task lighting in workspaces to ambient lighting in living areas. Moreover, the instant-on capability of LEDs ensures immediate brightness, enhancing convenience and usability in both residential and commercial settings.
Commonly Asked Questions to Address Any Uncertainties
Choosing the right light bulb is no longer a matter of simply picking up the cheapest option at the store. With the phase-out of incandescent and halogen bulbs due to their inefficiency, consumers are turning towards more energy-efficient solutions like LEDs.
LEDs, with their unmatched efficiency and long lifespan, are quickly becoming the go-to choice for all types of lighting needs. As technology continues to evolve, these bulbs not only offer brighter and more customizable lighting options but also play a crucial role in reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainability.
Ultimately, the shift towards efficient lighting is a positive change, making homes brighter, energy bills lower, and our environmental impact smaller. So next time you need to replace a light bulb, consider the long-term benefits and make the switch to energy-efficient lighting. Your future self—and the planet—will thank you.

